
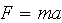 where
where

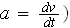 as it applies to a parachutist.
as it applies to a parachutist.
This lab investigates Newton's Law of motion which states that force equals
mass times acceleration
(
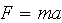 where
where

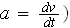 as it applies to a parachutist.
as it applies to a parachutist.
Since the parachutist is falling through air two forces come into play,
gravity and drag created by air resistance. These combine as follows:

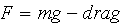 .
.

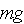 is by Newton's Law what would happen if something is falling in a vacumn and
the drag in this case is proportional to the velocity. It should be noted that
a qualified parachutist can vary the drag coefficient during freefall
noticeably. Combining these facts we have an ODE for velocity
:
is by Newton's Law what would happen if something is falling in a vacumn and
the drag in this case is proportional to the velocity. It should be noted that
a qualified parachutist can vary the drag coefficient during freefall
noticeably. Combining these facts we have an ODE for velocity
: 
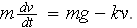
In this case the parachutist has a mass of

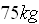 freefalls for
freefalls for

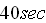 before opening the chute for another
before opening the chute for another

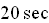 .
The drag coefficient for the chute is
.
The drag coefficient for the chute is

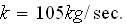 We will investigate what happens to the parachutist during the
We will investigate what happens to the parachutist during the

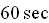 that he falls using various freefall drag coefficients.
that he falls using various freefall drag coefficients.
In each case use the freefall coef. for the first

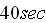 and
and
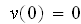 then on the same grid set
then on the same grid set

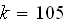 and the initial conditions at
and the initial conditions at

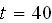 and the
and the

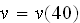 amount as read from the graph. Print the resulting graph in each case.
amount as read from the graph. Print the resulting graph in each case.
Freefall coefficients:
1.

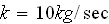
2.

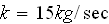
3.

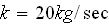
4.

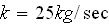
Now write a summary of your observations and a recommendation to the parachutist as to what should be happening when he deploys the chute (one page max).
This document created by Scientific Notebook 4.1.