Macroeconomics
Exam Date: Thurs., May 6, 2004
Instructions:
I) On your Scantron card you must print three things:
1) Print your full name clearly;
2) Print the day and time of your section (for example MWF 9);
3) Print the number I have written in ink on the upper right corner of
your copy of this test. (This number tells me which version of the
test you have. Without it your test cannot be graded properly and
you get no credit for your answers.)
II) Answer on your Scantron card, using a #2 pencil.
III) Warning: SOME QUESTIONS MUST BE ANSWERED SEVERAL
TIMES! Such questions will begin with a phrase such as this:
Repeat this answer on lines 37, 38 and 39.
Remember to do it!
IV) You must turn in this exam along with your Scantron card to get credit for
your score. Put your name on this exam.
Questions:
1. Identifying the effect of a tax cut on output and employment requires the use of:
A) positive economics.
B) the art of economics.
C) normative economics.
D) subjective economics.
2. Which economic groups competed for power during the transition from mercantilism to capitalism?
A) Craft guilds and industrialists.
B) Serfs and capitalists.
C) Craft guilds and the proletariat.
D) Capitalists and the proletariat.
3. Adam Smith believed that laissez-faire was in the interest of:
A) industrialists, whom he regarded as the most dynamic and progressive element in society.
B) the proletariat, who would receive higher wages.
C) the government, which would profit from higher taxes.
D) the general public.
4. Which of the following best describes state socialism?
A) Government sees to it that people work for the common good until they could be relied upon to do that on their own.
B) The invisible hand insures that individual decisions are made for the common good.
C) Government owns the means of production, but individual self-interest determines how production is organized.
D) Individuals are able to act in the best interest of everyone without direction from government or the invisible hand.
5. What form of business is the most common in the United States?
A) Non-profit businesses.
B) Corporations.
C) Sole proprietorships.
D) Partnerships.
6. Which of the following is a true statement?
A) The federal government relies primarily on income taxes; state and local governments rely to a greater extent on sales and property taxes.
B) The federal government relies primarily on sales and property taxes; state and local governments rely to a greater extent on income taxes.
C) The federal government relies primarily on excise and property taxes; state and local governments rely on sales taxes.
D) The federal government relies primarily on sales taxes; state and local governments rely on excise and property taxes.
7. On which of the following does the federal government spend the smallest amount?
A) Defense.
B) Income security.
C) Interest.
D) Health and education.
8. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 27.) The difference between the goods and services a country exports and those it imports is called:
A) the balance of trade.
B) a trade deficit.
C) a trade surplus.
D) the balance of payments.
9. The ratio of U.S. imports to U.S. GDP is about
A) 3 percent.
B) 14 percent.
C) 30 percent.
D) 60 percent.
10. Structural unemployment occurs when:
A) there is a general downturn in the economy.
B) people quit a job just long enough to look for and find another one.
C) people retire.
D) people lose a job because their skills become obsolete.
11. If the rate of unemployment equals the natural or target rate of unemployment, then:
A) actual output exceeds potential output.
B) real output equals nominal output.
C) potential output equals actual output.
D) real output exceeds nominal output.
12. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 28, 29 and 30.) If prices rose by 6% and real output fell by 3%, nominal output:
A) rose by 3%.
B) rose by 9%.
C) fell by 3%.
D) fell by 9%.
13. In a hyperinflation:
A) people hold as much money as possible because financial assets lose their value rapidly.
B) people continue to hold the same amount of money.
C) some people hold more money and some hold less.
D) people hold as little money as possible.
14. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 31.) Printing money:
A) can be used to finance the deficit but does add to the debt.
B) can be used to finance a deficit and does not affect the debt, unlike selling bonds.
C) can be used to finance a deficit and is superior to issuing bonds.
D) cannot be used to finance a deficit.
15. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 32, 33 and 34.) Bond holders:
A) lose when actual inflation is less than was expected.
B) lose when actual inflation is more than was expected.
C) lose when the expected inflation built into the nominal interest rate is correct.
D) do not lose when the expected inflation built into the nominal interest rate is lower than actual inflation.
16. As a percentage of GDP, U.S. budget deficits:
A) hit record levels in World War II.
B) hit record levels in the late 1980s and early 1990s.
C) declined steadily after World War II.
D) increased steadily after World War II.
17. By international standards, the U.S. debt to GDP ratio:
A) is negligible.
B) is relatively modest.
C) is relatively large.
D) is one of the highest in the world
18. Per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in the United States is roughly:
A) $20,000
B) $35,000
C) $70,000
D) $100,000
19. Malthus argued that because land was in fixed supply and labor was constantly increasing, economic growth would:
A) continue to accelerate.
B) slow but not stop.
C) eventually stop.
D) eventually become negative.
20. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 35 and 36.) Here are several statements about government debt and deficit spending.
1) Government should not borrow for current expenditures such as paper or electricity for government buildings, but can borrow for spending which will have lasting benefits, such as spending to educate a child, construct a national park or build a building. If the building will be useful for 50 years it is ok to borrow using a 50 year bond.
2) If the military is buying bullets which will be stored just in case there is a war, it is ok to borrow the money to buy them, but if the bullets are being purchased to be used for border patrol and target practise, then they should be paid for by taxes.
3) If the government wants to increase spending to stimulate the economy, since this will require increased borrowing it is better to spend the extra on new roads or new national parks rather than projects with little long term benefit.
Which of the following is the most complete and best answer?
A) Only statement 1 is correct.
B) Only statement 2 is correct.
C) Only statements 1 and 3 are correct.
D) Only statements 1 and 2 are correct.
E) All three statements are correct.
21. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 37 and 38.) There are difficulties with regulating the economy using an active monetary policy. Therefore most economists favor a "monetary regime" rather than a "monetary policy". Which of the following is the most accurate reaction to the above?
A) Correct.
B) The statement is false, and also the term "monetary regime" is not used in the text.
C) The statement is false because monetary regimes would be far too rigid and would prevent the FED from taking appropriate action. An active monetary policy is preferred by most economists.
D) Monetary policy is preferred over a monetary regime because a well stated policy will help prevent citizens from developing expectations of inflation.
E) Most economists don't care about this issue because they believe fiscal policy is the preferred tool for regulating the economy.
22. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 39 and 40.) Based on recent lectures concerning the impact of monetary policy on interest rates, if the Fed starts buying government bonds every year, creating steady reserve growth, your instructor believes
A) interest rates will fall and stay down, and starting in about 18-24 months prices will start rising. Interest rates will stay low and this inflation will continue unless the Fed stops buying bonds.
B) interest rates will fall at first, then starting in about 18-24 months prices will start rising, and as people come to expect the price inflation, interest rates will rise, perhaps above their original level. The high interest rates and the inflation will continue unless the Fed stops buying bonds.
C) inflation will begin in about 18-24 months, but eventually people will notice and come to expect the inflation, so the social costs of the inflation will disappear and the inflation will subside.
D) Fed purchases of bonds affect fiscal policy, not monetary policy. There is no influence on the money supply, inflation or interest rates.
Use the following to answer question 23:
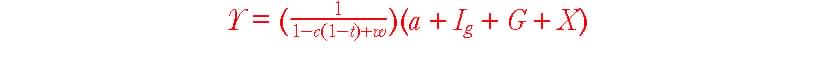
23. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 41, 42 and 43.) (You may refer to the equation above.) Choose the most complete answer. Using the Keynesian multiplier model and assuming it gives correct answers, if a recession abroad reduces exports by $100 billion per year while and a U.S. recession causes a $100 billion per year collapse in gross investment spending, and unemployment insurance increases autonomous consumption expenditures ("a" in the equation) by $50 billion, then
A) Both C and E are true.
B) Both C and D are true.
C) The economy will experience a recession.
D) The economy will experience no recession provided government spending is increased by $150 billion.
E) The economy will experience no recession provided government spending is increased by $100 billion.
24. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 44, 45 and 46.) Choose the best answer. When the government spends more than its tax proceeds the result is a deficit, and government borrowing. Your instructor believes:
A) government borrowing is never desirable.
B) borrowing is desirable if the government will spend the money on something which will yield benefits for a long time, for example winning an important war or creating a national park.
C) government borrowing caused by tax cuts can be an important stimulus to help bring the economy out of a recession.
D) borrowing is always desirable because if the government runs a surplus it is creating a deflationary gap.
E) borrowing is desirable if the proceeds will be spent on an important annual activity, such as the annual fireworks display.
Use the following to answer question 25:

25. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 47 and 48.) In the money supply equation just above, assume that CT = 50; Tf = 130, Lf = 20; rd, rt, sd and st = 1; rct = .5 and rcd = .5. Then the "money multiplier" is:
A) 120
B) 5
C) .6
D) 200
E) A, B and D combined
26. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 49 and 50.) If, in the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply model (as presented in the text and lecture) the two curves intersect to the right of Potential Output,
1) There is a "deflationary gap".
2) Prices and wages will begin to rise, shifting the AS curve upward.
A) Only statement 1 is correct.
B) Only statement 2 is correct.
C) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
D) Neither statement 1 nor 2 is correct.
Answer Key -- S04FinalExam
1. A positive economics.
Origin: Chapter 1: Economics and Economic.......132
2. A Craft guilds and industrialists.
Origin: Chapter 2: Economic Organization of.......141
3. D the general public.
Origin: Chapter 2: Economic Organization of.......142
4. A Government sees to it that people work for the common good until they could be relied upon to do that on their own.
Origin: Chapter 2: Economic Organization of.......147
5. C Sole proprietorships.
Origin: Chapter 3: U.S. Economy in a Global.......31
6. A The federal government relies primarily on income taxes; state and local governments rely to a greater extent on sales and property taxes.
Origin: Chapter 3: U.S. Economy in a Global.......62
7. D Health and education.
Origin: Chapter 3: U.S. Economy in a Global.......64
8. A the balance of trade.
Origin: Chapter 3: U.S. Economy in a Global.......79
9. B 14 percent.
Origin: Chapter 3: U.S. Economy in a Global.......92
10. D people lose a job because their skills become obsolete.
Origin: Chapter 6: Economic Growth, Business.......58
11. C potential output equals actual output.
Origin: Chapter 6: Economic Growth, Business.......99
12. A rose by 3%.
Origin: Chapter 6: Economic Growth, Business.......138
13. D people hold as little money as possible.
Origin: Chapter 6: Economic Growth, Business.......145
14. B can be used to finance a deficit and does not affect the debt, unlike selling bonds.
Origin: Chapter 12: The Politics of Deficits.......22
15. B lose when actual inflation is more than was expected.
Origin: Chapter 12: The Politics of Deficits.......52
16. A hit record levels in World War II.
Origin: Chapter 12: The Politics of Deficits.......94
17. B is relatively modest.
Origin: Chapter 12: The Politics of Deficits.......102
18. B $35,000
Origin: Chapter 7: National Income Accounting....122
19. C eventually stop.
Origin: Chapter 8: Growth, Productivity, and.......88
20. E All three statements are correct.
Origin: GTA Questions....34
21. A Correct.
Origin: GTA Questions....50
22. B interest rates will fall at first, then starting in about 18-24 months prices will start rising, and as people come to expect the price inflation, interest rates will rise, perhaps above their original level. The high interest rates and the inflation will continue unless the Fed stops buying bonds.
Origin: GTA Questions....59
23. B Both C and D are true.
Origin: GTA Questions....60
24. B borrowing is desirable if the government will spend the money on something which will yield benefits for a long time, for example winning an important war or creating a national park.
Origin: GTA Questions....63
25. C .6
Origin: GTA Questions....68
26. B Only statement 2 is correct.
Origin: GTA Questions....77