Human Urinary Bladder
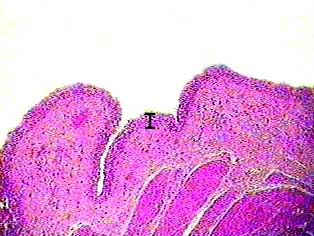
This image shows part of the wall of the urinary bladder. The bar shows the location and thickness of the transitional epithelium that lines the urinary bladder. The layer of tissue just underneath the epithelium is connective tissue, and at the bottom of the image you can see some smooth muscle tissue.
Human Urinary Bladder
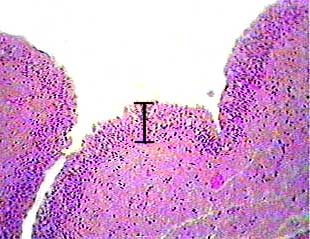
The bar indicates the thickness of the transitional epithelium.
Human Urinary Bladder
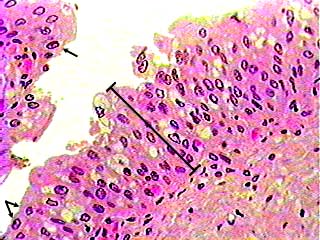
Transitional epithelium is a stratified tissue in which the cells are all have a fairly round shape when the organ it lines is not distended (stretched out). The image shows the wall of the urinary bladder in the relaxed state (not distended). When the tissue is stretched, the cells, especially those on the surface, become flat. This allows organs lined with transitional epithelium to change shape without damaging the epithelial lining. The arrows in the lower left corner of the image point to typical unstretched transitional epithelial cells.