Human aorta c.s.
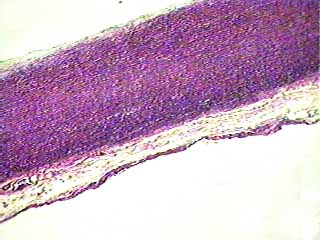
True elastic connective tissue is very rare, and we have no slide specimens that show it. But elastic fibers are present in relatively high concentration in several organs, including the largest arteries in the body. This image shows a portion of the wall of the aorta, the large vessel that carries blood from the heart to the body. Because elastin fibers are so important in the recoil of organs like arteries and lungs, we decided that you should know what they look like.
Human aorta c.s
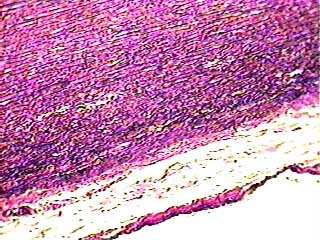
At this magnification you can see black wavy lines. Those are the elastin fibers. When an organ containing these fibers is stretched, the elastin fibers recoil (go back to their original length) and pull the organ back into shape.
Human aorta c.s
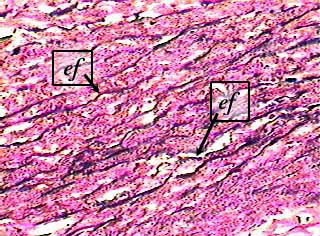
The labels indicate individual elastin fibers (ef) in the aorta.
The areas stained pink (between the elastin fibers) contain smooth muscle cells, reticular fibers, and ground substance.