 Blood is an unusual connective
tissue because it is normally in liquid form. It consists of
a fluid called plasma and cells (formed elements) that are suspended
in the plasma. The slide from which this image was prepared was
a blood smear--it was made by putting a drop of blood on one
end of a slide, and using a second slide to spread the blood
into a thin, uniform layer over the slide. Some smears are better
than others, meaning that the cells are more evenly spread out.
Never use the part of a blood smear slide where cells are piled
up on top of each other. Look for part of the slide where the
cells are in a single layer. You can do that while you are using
the 4X objective lens because you can see a larger area of the
slide that way.
Blood is an unusual connective
tissue because it is normally in liquid form. It consists of
a fluid called plasma and cells (formed elements) that are suspended
in the plasma. The slide from which this image was prepared was
a blood smear--it was made by putting a drop of blood on one
end of a slide, and using a second slide to spread the blood
into a thin, uniform layer over the slide. Some smears are better
than others, meaning that the cells are more evenly spread out.
Never use the part of a blood smear slide where cells are piled
up on top of each other. Look for part of the slide where the
cells are in a single layer. You can do that while you are using
the 4X objective lens because you can see a larger area of the
slide that way.
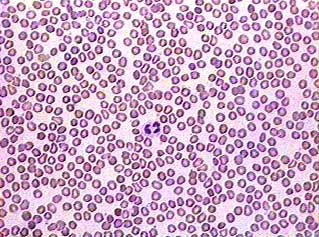 Using the 10X objective lens you
can see individual cells and tell the difference between red
and white blood cells. You can even see platelets if you know
what to look for. The platelets on this image are very faint,
but you can see them in the image below.
Using the 10X objective lens you
can see individual cells and tell the difference between red
and white blood cells. You can even see platelets if you know
what to look for. The platelets on this image are very faint,
but you can see them in the image below.
Most of the cells you see here are erythrocytes or red blood
cells. They are small and don't have a nucleus. They are thin
in the middle, and look like red doughnuts in this image. The
leukocytes (white blood cells) are larger than red blood cells
and they have nuclei that stain dark purple. Many of the white
blood cells have segmented nuclei, meaning that the nucleus is
pinched into two or more smaller parts that are still connected
to each other (sort of like when you twist one of those long
balloons to make a sculpture). Can you find the white blood cell
in this image? Its nucleus has two segments.
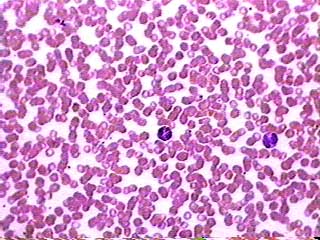 The red blood cells in this image
are stacked up on top of each other. We included it to show you
what an unacceptable smear looks like! But it does have the advantage
of including two kinds of white blood cell that are different
from the one seen in the image above. The leukocyte on the left
has many very dark granules in its cytoplasm. The granules are
so dark that you can't see the nucleus. The leukocyte on the
right has a two-lobed nucleus and reddish-orange granules in
its cytoplasm. Consult your textbook to find out what they are.
The red blood cells in this image
are stacked up on top of each other. We included it to show you
what an unacceptable smear looks like! But it does have the advantage
of including two kinds of white blood cell that are different
from the one seen in the image above. The leukocyte on the left
has many very dark granules in its cytoplasm. The granules are
so dark that you can't see the nucleus. The leukocyte on the
right has a two-lobed nucleus and reddish-orange granules in
its cytoplasm. Consult your textbook to find out what they are.
The thrombocytes, or platelets, do how show very well in these
images. You can see them if you look very carefully between the
other cells. They will look like small purple dots.