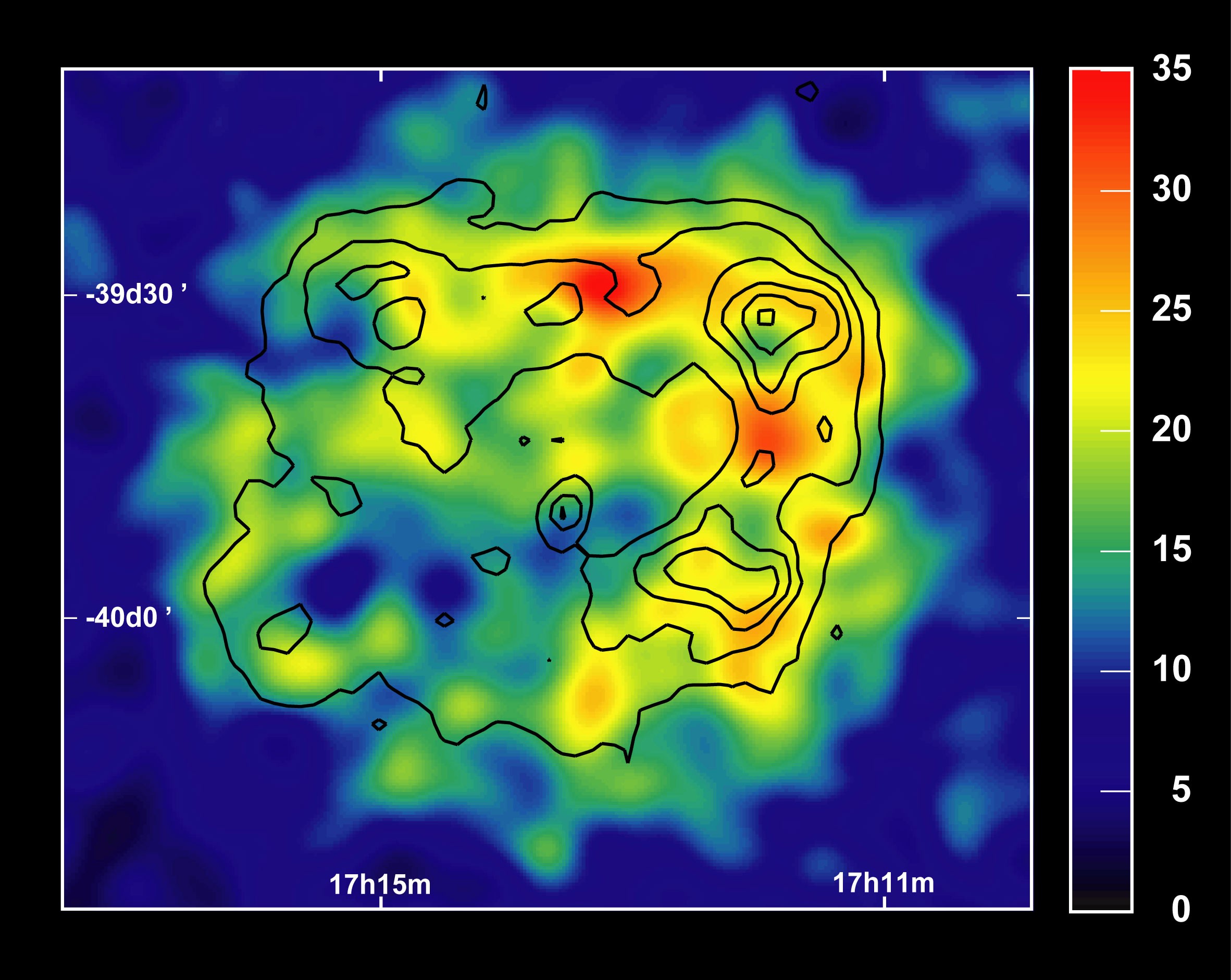
 |
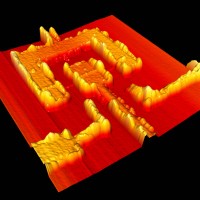
Atomic Force Microscopy image of the World smallest Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) ever, recently fabricated at CEMES (thanks to the access provided to LAAS-RTB platform facilities) under a partnership with Institut Néel (Grenoble). The sensitive part of the device is a single single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT, diameter ~1.4 nm) which is contacted at three different places by superconducting bimetallic (aluminum/palladium) leads (arrows). The specific behaviour of the two uncoated SWNT parts, called Josephson junctions (between the arrows), makes the device 1012 times more sensitive to magnetic fields than a regular SQUID, making possible the measurement of magnetic fields at the level of a single molecule.
http://www.cemes.fr/r7_english/r2_rech/r2_sr4_nmat/th4_or2.htm
|