Final Exam Exam Date: Wed-Fri, May 5-7, 2004
Instructions:
I) On your Scantron card you must print three things:
1) Print your full name clearly;
2) Print the day and time of your section (for example MW 1:25);
3) Print the number I have written in ink on the upper right corner of
your copy of this test. (This number tells me which version of the
test you have. Without it your test cannot be graded properly and
you get no credit for your answers.)
II) Answer on your Scantron card, using a #2 pencil.
III) Warning: SOME QUESTIONS MUST BE ANSWERED SEVERAL
TIMES! Such questions will begin with a phrase such as this:
(Repeat answer on lines 37, 38 and 39)
Remember to do it!
IV) You must turn in this printed exam along with your Scantron card, otherwise
your score in this exam is "F".
Questions:
1. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 24 and 25.) According to the "shut-down rule",
A) a firm should keep operating in the short run as long as the demand curve is somewhere above short run average variable cost curve, and shut down in the long run if the demand curve is nowhere above the long run average cost curve.
B) all the other answers are correct.
C) a firm should keep operating in both the long run and the short run if the demand curve is somewhere above both the long run average cost curve and the short run average variable cost curve.
D) a firm should shut down at night, but operate during the day, if the demand curve at night is everywhere below the short run average variable cost curve and the demand curve during the day is somewhere above both the long run average cost curve and the short run average variable cost curve.
E) a firm should shut down both in the short run and in the long run if the demand curve is everywhere below both the long run average cost curve and the short run average variable cost curve.
2. With regard to voluntary solutions to environmental problems, economists believe that:
A) these are the most effective ways to solve existing problems.
B) these are often ineffective due to the free-rider problem.
C) no one would ever cooperate.
D) everyone would cooperate, but it isn't fair to ask individuals to make sacrifices.
3. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 26.) NAFTA:
A) is an organization that loans money to countries in financial crises.
B) is the body that governs international trade and resolves international trade disputes.
C) is the free trade agreement that governs trade among the 15 members of the European Union.
D) reduces barriers to international trade within North America
4. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 27 and 28.) All of the following are characteristics of public goods except:
A) they are nonexclusive.
B) once provided, public goods are available to non-buyers.
C) they are nonrival in consumption.
D) unlike private goods, public goods can only be consumed once.
5. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 29 and 30.) For an externality to occur:
A) a third party must be affected, either positively or negatively.
B) pollution must occur.
C) someone must have been physically hurt.
D) a spill-over cost must have occurred.
6. If money did not exist in a modern economy,
A) production would be much lower and the average person would be extremely poor.
B) specialization and the division of labor could be carried to a much higher level, resulting in a much more smoothly functioning economy.
C) the world would not go around.
D) barter would be extremely rare.
E) none of the other answers.
7. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 31.) The supply of leather jackets would be expected to increase as a result of:
A) an increase in the cost of producing leather jackets.
B) an increase in the price of leather jackets.
C) an increase in the popularity of leather jackets.
D) the expectation that the price of leather jackets will fall in the future.
8. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 32 and 33.) Which of the following is not considered a source of market failure?
A) Public goods.
B) Imperfect information.
C) Profit-maximizing behavior.
D) Externalities.
9. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 34.) Public choice economists argue that rent-seeking activities:
A) never succeed in transferring surplus from one group to another.
B) benefit the middle class at the expense of the upper class.
C) are significant and result in a net loss to society.
D) are productive expenditures from society's perspective.
10. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 35.) The supply curve is likely to be most elastic in which period?
A) The instantaneous period.
B) The short run.
C) The long run.
D) The momentary period.
Use the following to answer question 11:

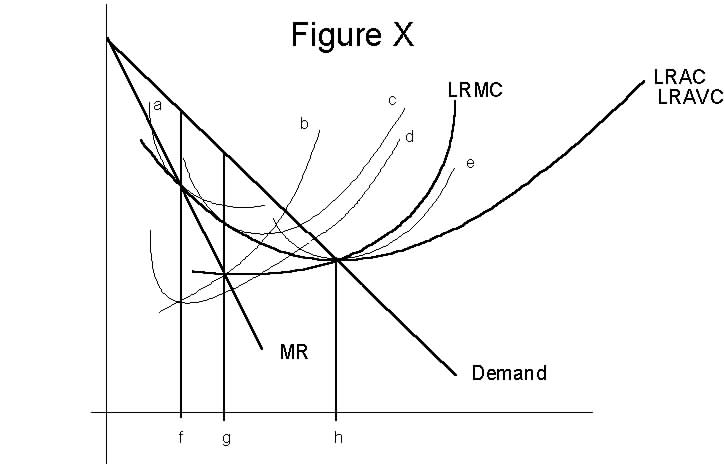
11. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 36.) In Figure X (just above),
A) curve 'b' is an average variable cost curve and 'a' is a short run average cost curve.
B) curves 'a', 'c' and 'e' are long run average cost curves.
C) curve 'd' is a short run average cost curve and 'b' is a short run marginal cost curve.
D) curve 'c' is a short run average cost curve and 'd' is an average variable cost curve.
E) this firm should run in the long run but shut down in the short run.
Use the following to answer question 12:

12. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 37.) In Figure X, this monopolist will
1) produce output "f".
2) produce output "g".
3) produce output "h".
4) use short run average cost curve "a".
5) use short run average cost curve "c".
6) use short run average cost curve "e".
7) keep operating in the long run.
A) Only statements 1 and 4 correct.
B) Only statements 1, 4 and 7 are correct.
C) Only statements 2 and 5 are correct.
D) Only statements 2, 5 and 7 are correct.
E) Only statement 7 is correct.
Use the following to answer question 13:

13. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 38.) Select the best lettered answer after evaluating the following statements. Refer to the figure above as needed.
1) If price discrimination is not possible, this monopolist will choose the monopoly price ph (the highest price of the four choices shown) and output level "a".
2) If this monopolist is able to price discriminate by charging two different prices, one being the original monopoly price and the second being price pl, then society's "efficiency cost" (welfare cost) from this monopoly will be smaller than if the monopolist had to charge just one price.
3) If this firm must charge just one price, and if society wishes to eliminate the "efficiency cost" of this monopoly, this can be accomplished by forcing the price down to price pm.
A) Only statement 1 is correct.
B) Only statement 2 is correct.
C) Only statement 3 is correct.
D) Two of the statements are correct.
E) All of the statements are correct, or none of them are correct.
14. Kuo S. Huang estimates that with every 10% increase income, the quantity of turkey purchased declines by 1.2%. From this information one would conclude that:
A) all answers are correct.
B) if income drops by 5%, the demand for turkey will rise by roughly .6%
C) turkey is an inferior good.
D) if the demand for turkey has declined by 2.4%, this could be caused by a rougly 20% increase in income.
E) if incomes rise while the price of turkey falls, the quantity or turkey demanded, taking both effects into account, may either rise or fall.
15. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 39.) Evaluate each of the following statements having to do with international flows of capital and international flows of goods, then select the best answer from among A though D below.
1) As a practical matter, financial claims cannot move between nations as quickly as goods. That is why the foreign exchange markets are linked more tightly to the trade currency exchange rates of internationally traded goods than internationally traded claims.
2) Since a country can have an imbalance between the import and export of claims (in other words, can run a capital account surplus or deficit) therefore a country can run a surplus or deficit in its balance of payments.
A) Only statement 1 is true.
B) Only statement 2 is true.
C) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
D) Neither statement 1 nor 2 is true.
16. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 40.) Evaluate each of the following statements having to do with the international foreign exchange markets, then select the best answer from the lettered choices below.
1) Without the foreign exchange markets (by which citizens all over the world acquire the foreign money they need for purchases of the goods of foreign nations) international trade would not be possible.
2) The exchange rates in the international foreign exchange markets track the trade currency ratios of internationally traded claims more closely than the trade currency ratios of internationally traded goods.
A) Only statement 1 is true.
B) Only statement 2 is true.
C) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
D) Neither statement 1 nor 2 is true.
17. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 41.) Assume that the income elasticity of demand for a good is positive. Then evaluate each of the following statements and choose the best answer from among the lettered choices below.
1) The good is a luxury good.
2) The good is a necessity.
3) The good is a normal good.
4) The good is an inferior good.
A) Statement 3 is correct, and also either Statement 1 or Statement 2, but not both.
B) Statements 3 and 4 are correct.
C) Statement 1 is correct, but none of the others.
D) Statement 3 is correct, but none of the others.
E) Statement 4 is correct.
18. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 42.) Evaluate each of the following statements having to do with international trade, then select the best from the lettered choices below.
1) There are no "pareto gains" from international trade of goods between nations, because the process of international trade always creates losers, as well as gainers, in both countries.
2) Suppose a small country began international trade of goods with a large, economically advanced country such as the United States, and suppose further that neither country was permitted to impose protective tarriffs. Then most of the pareto gains from international trade are likely to be captured by the larger, more advanced country and in fact, the smaller country might not benefit at all.
A) Only statement 1 is true.
B) Only statement 2 is true.
C) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
D) Neither statement 1 nor 2 is true.
Use the following to answer question 19:

19. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 43 and 44.) Refer to the graphs above. In graphs B and D:
A) the tax revenue collected by the government is smaller than in the other graphs.
B) the dead weight loss associated with the tax is the smallest.
C) there is no producer surplus with or without the tax.
D) there is no consumer surplus with or without the tax.
20. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 45.) If elasticity of demand is 0.5, elasticity of supply is 0.2, and a 10% excise tax is levied on the good:
A) the tax burden on suppliers will be greater.
B) the tax burden on consumers will be greater.
C) the tax burden will be the same for both.
D) one cannot say who will bear the greater burden without knowing the tax.
21. (Repeat your answer on Scantron line 46.) One advantage of the Herfindahl index over the concentration ratio measure is that:
A) it gives extra weight to a single firm that has an especially large share of the market.
B) it is the most commonly used concentration ratio.
C) it only tells about the top 50 firms in an industry.
D) it is easier to gather the data to calculate.
Use the following to answer questions 22-23:
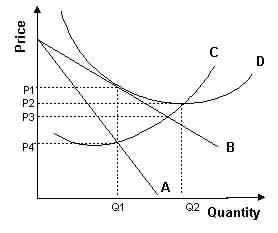
22. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 47 and 48.) Refer to the graph above. To maximize profit, the firm represented by this graph will:
A) produce Q1 and set price equal to P1.
B) produce Q1 and set price equal to P3.
C) produce Q1 and set price equal to P4.
D) produce Q2 and set price equal to P2.
23. (Repeat your answer on Scantron lines 49 and 50.) Refer to the graph above. According to the graph, economic profit is currently:
A) impossible to determine.
B) positive.
C) negative.
D) zero.
Answer Key -- Final Exam S04a
1. B all the other answers are correct.
Origin: Cool Questions fr Micro....56
2. B these are often ineffective due to the free-rider problem.
Origin: Chapter 15: Government Policy and.......74
3. D reduces barriers to international trade within North America
Origin: Cool Questions fr Micro....21
4. D unlike private goods, public goods can only be consumed once.
Origin: Chapter 15: Government Policy and.......117
5. A a third party must be affected, either positively or negatively.
Origin: Chapter 15: Government Policy and.......30
6. A production would be much lower and the average person would be extremely poor.
Origin: Cool Questions fr Micro....3
7. D the expectation that the price of leather jackets will fall in the future.
Origin: Cool Questions fr Micro....28
8. C Profit-maximizing behavior.
Origin: Chapter 15: Government Policy and.......23
9. C are significant and result in a net loss to society.
Origin: Cool Qs for Comprehensive Final....76
10. C The long run.
Origin: Cool Qs for Comprehensive Final....65
11. D curve 'c' is a short run average cost curve and 'd' is an average variable cost curve.
Origin: Cool Questions fr Micro....35
12. D Only statements 2, 5 and 7 are correct.
Origin: GTA Micro Questions....58
13. B Only statement 2 is correct.
Origin: GTA Micro Questions....57
14. A all answers are correct.
Origin: Cool Questions fr Micro....57
15. D Neither statement 1 nor 2 is true.
Origin: GTA Micro Questions....53
16. B Only statement 2 is true.
Origin: GTA Micro Questions....54
17. A Statement 3 is correct, and also either Statement 1 or Statement 2, but not both.
Origin: GTA Micro Questions....56
18. D Neither statement 1 nor 2 is true.
Origin: GTA Micro Questions....55
19. B the dead weight loss associated with the tax is the smallest.
Origin: Chapter 7: Taxation and Government.......79
20. A the tax burden on suppliers will be greater.
Origin: Chapter 7: Taxation and Government.......83
21. A it gives extra weight to a single firm that has an especially large share of the market.
Origin: Chapter 13: Monopolistic Competition.......26
22. A produce Q1 and set price equal to P1.
Origin: Chapter 13: Monopolistic Competition.......82
23. D zero.
Origin: Chapter 13: Monopolistic Competition.......83