Your Name:
_____________________________
Class: Microeconomics (Sections 10-12; MW and TTh)
Exam 2 Exam Dates: Wednesday-Thursday, October 30-31, 2002
Instructions:
I) On your Scantron card you must
print three things:
1) Print your full name clearly;
2) Print the day and time of your
section (for example MW 1:25);
3) Print the number I have written
in ink on the upper right corner of
your copy of this test. (This
number tells me which version of the
test you have. Without it your
test cannot be graded properly and
you get no credit for your answers.)
II) Answer on your Scantron card, using a #2
pencil.
III) Warning:
SOME QUESTIONS MUST BE ANSWERED SEVERAL
TIMES!
Such questions will begin with a phrase such as this:
(Repeat answer on lines 37, 38
and 39)
Remember to do it!
Questions:
Use the
following to answer question 1:

1. (Repeat answer on line 27) Refer to the graph above. Given a tax of t on suppliers, revenue
collected is:
A) B and C.
Suppliers pay B. Consumers pay
C.
B) B and C.
Suppliers pay C. Consumers pay
B.
C) A, B and C.
Suppliers pay A. Consumers pay
B.
D) A, B and C.
Suppliers pay B. Consumers pay
A.
2. (Repeat answer on lines 28 and 29) Social welfare is maximized when price
equals:
A) marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue.
C) average total cost.
D) average variable cost.
3. Patents are given on new inventions to:
A) help firms earn positive economic profit.
B) encourage firms to devote resources to the
development of new inventions.
C) prevent firms from earning positive economic
profits.
D) guarantee that the products created by new
inventions are affordable to consumers.
Use the
following to answer question 4:

4. (Repeat answer on lines 30 and 31) Refer to the graph above. If the wage
for soldiers is set too low at P = 6, a military draft will be needed to
satisfy the demand for soldiers, and the resulting dead weight loss (also known
as the "welfare loss" or efficiency loss) will be equal to:
A) 120.
B) 320.
C) 480.
D) 720.
5. (Repeat answer on line 32) The profit-maximization assumption of
economic theory is an imperfect fit for reality because:
A) all real firms want to maximize long-term
profits rather than short-run profits.
B) all real firms want to maximize their share
of the market.
C) all real firms want to maximize their sales
growth rate.
D) often the decision makers of a firm are not
its owners, but are instead managers with their own priorities.
6. Having government buy patent rights has been
suggested as an alternative to regulating the price charged by a patent-holding
monopolist. The major benefit of this approach is that:
A) government would have to increase taxes to
cover the cost of the buyout.
B) it would be difficult for government to
determine which patents to buy.
C) it could have negative incentive effects.
D) it would maintain the incentive for companies
to engage in research and development.
7. Which of the following statements best
summarizes the text's conclusions regarding the likelihood of technological
innovation in a monopolized industry?
A) Monopolies earn the profits needed for
research and development and have the strongest incentive to innovate.
B) Monopolies may earn the profits needed for
research and development, but they seldom have the incentive to innovate.
C) Monopolies seldom earn the profits needed for
research and development, but they have the strongest incentive to innovate.
D) Monopolies seldom earn the profits needed for
research and development and they have no incentive to innovate.
Use the
following to answer question 8:
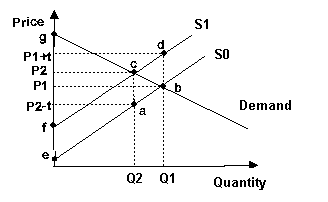
8. Refer to the graph above. Assume the market
is initially in equilibrium at price P1. If government imposes a per unit tax
equal to the distance from point a to point c in the graph, the welfare loss triangle
from this tax is equal to area:
A) cfg.
B) beg.
C) abc.
D) bcd.
9. (Repeat answer on line 33) The market structure in which many
different firms supply similar, but slightly differentiated products, is:
A) monopoly.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopolistic competition.
D) perfect competition.
10. If the response of quantity demanded to a
change in price is infinitely large, the burden of a tax on suppliers is borne:
A) entirely by the suppliers.
B) entirely by the consumers.
C) mostly by the suppliers, and partly by the
consumers, if the demand curve is inelastic.
D) partly by the suppliers, and mostly by the
consumers, if the demand curve is elastic.
11. Which of the following is the result of the
monitoring problem?
A) A firm successfully erases all evidence of
illegal activity.
B) Insufficient data is available to prosecute
two colluding firms.
C) U.S. managers' salaries are about four times
that of comparable managers in Japan.
D) A firm emits pollution that costs the
government money to clean up.
12. (Repeat answer on lines 34 and 35) An
important difference between price ceilings and taxes is that price ceilings
__________ and taxes __________.
A) create shortages; do not
B) create shortages; result in no dead weight
loss
C) result in dead weight loss; do not
D) result in dead weight loss; create shortages
13. Long-run equilibrium for firms in
monopolistically competitive industries is similar to that for firms in perfect
competition in that:
A) price equals minimum possible average total
cost.
B) price equals marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue equals average total cost.
D) economic profit equals zero.
14. (Repeat answer on line 36 and 37) X-inefficient firms:
A) are prevented from operating efficiently by
government regulations.
B) make higher profits by operating
inefficiently than would be possible by operating efficiently.
C) are owned by individuals who are not
interested in profits.
D) operate less efficiently than they are
technically capable of producing.
15. If the supply curve is vertical the burden of
a tax on suppliers is borne:
A) entirely by the suppliers.
B) entirely by the consumers.
C) mostly by the suppliers, and partly by the
consumers, if the demand curve is inelastic.
D) partly by the suppliers, and mostly by the
consumers, if the demand curve is elastic.
16. (Repeat answer on lines 38, 39, 40 and 41) As discussed in lecture the following
statement(s) is/are true about the welfare cost of price discrimination
compared to the price welfare cost of monopoly:
A) If the price discriminator only charges prices
above the monopoly price, welfare costs are likely to be larger than for
monopoly.
B) If the price discriminator only charges
prices which are equal to or lower than the monopoly price, welfare costs will
definitely be lower than for monopoly.
C) If the price discriminator charges prices
which are both higher and lower than the monopoly price, welfare costs will be
be less than for monopoly.
D) Three of the other answers are correct.
E) A is wrong, but B and C are definitely right.
17. In the United States lobbying is:
A) not important to most monopolies.
B) one of the tools used by firms to acquire a
monopoly.
C) illegal.
D) important to firms in perfectly competitive
markets.
18. In a constant-cost industry, long-run market
supply is:
A) downward-sloping.
B) horizontal.
C) upward-sloping.
D) vertical.
Use the
following to answer question 19:
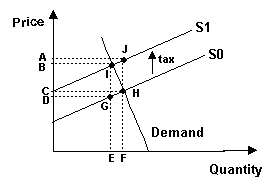
19. Refer to the graph above. Initial market
equilibrium is at point H. When government imposes a per unit tax, supply
shifts from S0 to S1. The effect of this tax is to:
A) raise the price consumers pay from D to C.
B) raise the price consumers pay from C to A.
C) raise the equilibrium quantity sold from E to
F.
D) raise the price sellers charge from C to B.
20. (Repeat answer on line 42) The problem of technological lock-in
occurs because:
A) more efficient technologies replace less
efficient ones.
B) less efficient technologies replace more
efficient ones.
C) prior use of a technology makes the adoption
of subsequent technologies difficult.
D) prior use of a technology makes the rewards
for subsequent innovations greater.
21. (Repeat answer on line 43) A(n) __________ contract is defined as
an agreement in which the incentives of both parties match their goals as
closely as possible.
A) X-inefficiency
B) monitoring
C) incentive-compatible
D) corporate takeover
22. Cost-conscious consumers use cents-off
coupons when purchasing items such as soap or frozen dinners. As a result, they pay a lower price. This is an example of:
A) welfare loss.
B) breaking even.
C) quantity discrimination.
D) price discrimination.
23. (Repeat answer on line 44 and 45) The cartel model of oligopoly assumes
that:
A) a monopoly acts as if it is an oligopoly.
B) oligopolies act as if they were perfectly
competitive.
C) oligopolies act as if they were monopolists.
D) monopolistically competitive firms act as if
they were monopolists.
24. Collusion is most likely occur in a(n):
A) monopoly.
B) oligopoly.
C) monopolistically competitive industry.
D) perfectly competitive industry.
25. (Repeat answer on lines 46, 47 and
48) __________ activities are
designed to transfer surplus from one group to another.
A) Welfare
B) Surplus
C) External
D) Rent-seeking
26. (Repeat answer on lines 49 and 50) The demand curve faced by a perfectly
competitive firm is the same as:
A) its marginal cost curve.
B) its marginal revenue curve.
C) its average total cost curve.
D) its average fixed cost curve.
Answer Key -- MicroEc Ex 2--Taxes + Market
Theory
1. A B
and C. Suppliers pay B. Consumers pay C.
LO: 7-3
Page: 162
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....12
2. A marginal
cost.
LO: 12-5
Page: 270
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....47
3. B encourage
firms to devote resources to the development of new inventions.
LO: 12-7
Page: 274
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....54
4. A 120.
LO: 7-4
Page: 167
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....15
5. D often
the decision makers of a firm are not its owners, but are instead managers with
their own priorities.
LO: 14-1
Page: 306
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....75
6. D it
would maintain the incentive for companies to engage in research and
development.
LO: 12-7
Page: 274
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....57
7. B Monopolies
may earn the profits needed for research and development, but they seldom have
the incentive to innovate.
LO: 14-6
Page: 319
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....87
8. C abc.
LO: 7-1
Page: 159
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....2
9. C monopolistic
competition.
LO: 13-2
Page: 286
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....61
10. A entirely
by the suppliers.
LO: 7-3
Page: 161
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....7
11. C U.S.
managers' salaries are about four times that of comparable managers in Japan.
LO: 14-1
Page: 307
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....78
12. A create
shortages; do not
LO: 7-4
Page: 165
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....11
13. D economic
profit equals zero.
LO: 13-3
Page: 289
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....67
14. D operate
less efficiently than they are technically capable of producing.
LO: 14-2
Page: 308
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....80
15. A entirely
by the suppliers.
LO: 7-3
Page: 161
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....9
16. D Three
of the other answers are correct.
LO: (None)
Page: (None)
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....55
17. B one
of the tools used by firms to acquire a monopoly.
LO: 14-4
Page: 314
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....84
18. B horizontal.
LO: 11-7
Page: 254
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....29
19. D raise
the price sellers charge from C to B.
LO: 7-1
Page: 158
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....5
20. C prior
use of a technology makes the adoption of subsequent technologies difficult.
LO: 14-6
Page: 321
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....91
21. C incentive-compatible
LO: 14-1
Page: 307
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....76
22. D price
discrimination.
LO: 12-4
Page: 269
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....44
23. C oligopolies
act as if they were monopolists.
LO: 13-5
Page: 292
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....72
24. B oligopoly.
LO: 13-5
Page: 292
Origin:
GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....74
25. D Rent-seeking
LO: 7-5
Page: 167
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....16
26. B its
marginal revenue curve.
LO: 11-2
Page: 242
Origin: GTA Subset--Taxes + Market Thy....25