Phenylalanine Deaminase Test
Phenylalanine deaminase medium tests the ability of an organism to produce the enzyme deaminase. This enzyme removes the amine group from the amino acid phenylalanine and releases the amine group as free ammonia. As a result of this reaction, phenylpyruvic acid is also produced.
Phenylalanine agar, also known as phenylalanine deaminase medium, contains nutrients and DL-phenylalanine. It is used to differentiate members of the genera Proteus, Morganella (which were originally classified under the genus Proteus), and Providencia from other Enterobacteriaceae.
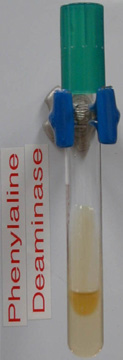
After incubation, 10% ferric chloride is added to the media; if phenylpyruvic acid was produced, it will react with the ferric chloride and turn dark green. If the medium remains a straw color, the organism is negative for phenylalanine deaminase production.
 |
 |
When 10% ferric chloride is added to phenylalanine deaminase medium inoculated with Proteus mirabilis, the presence of phenylpyruvic acid causes the media to turn dark green. This is a positive result. |
When 10% ferric chloride is added to phenylalanine deaminase medium inoculated with Staphylococcus aureus, no color change occurs. This is a negative result. |
